ElectricGrid
The TransiEnt library is an award-winning, open-source Modelica library designed for modeling complex energy systems.
This case study specifically showcases how to seamlessly integrate control logic into an existing energy system model. This model consists of 1992 variables and equations, reflecting its complexity and realism in simulating the operation of a real-world grid.
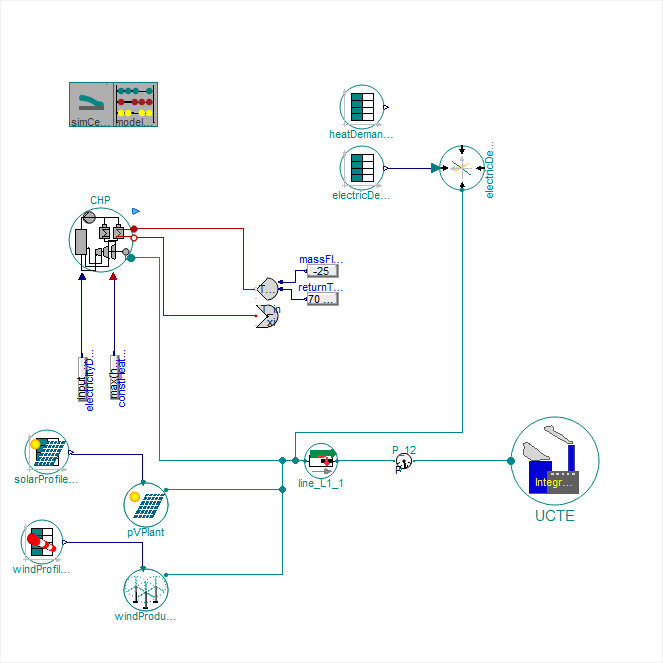
This model represent a simulation of an electrical grid system, incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar panels (bottom left), wind plants (bottom left), and a Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plant (left) into an electric grid (bottom right) that serves user demands (top right). The system is designed to balance power production from various sources with the dynamic energy demand from consumers.
Control Logic
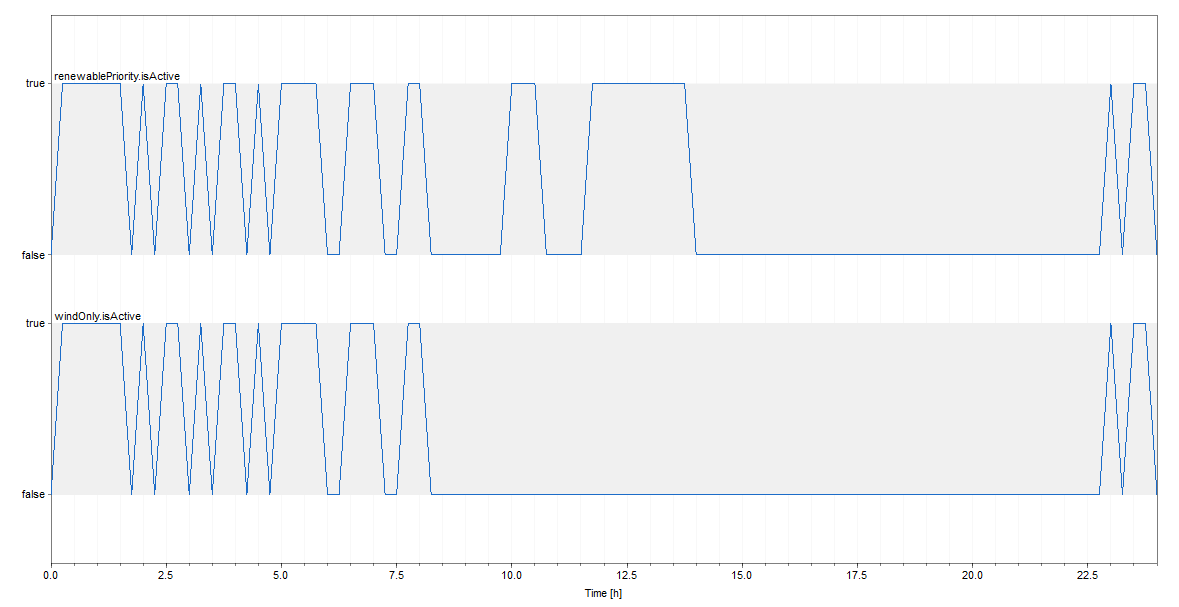
In this case study, a renewablePriority context and a windOnly context were added to the original electrical grid model. Both contexts are condition-based and are weakly included.
When the renewablePriority context is active, the Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plant stops operating. When the windOnly context is active, only wind energy is used. Since the windOnly context is weakly included within the renewablePriority context, the CHP plant also stops operating when the windOnly context is active.
As the results indicate, activating or deactivating the windOnly context also activates or deactivates the renewablePriority context.